Ecology Made Simple
Connecting You with the Wild
Dive into the fascinating realms of ecology and wildlife with us. Our blog is dedicated to exploring the intricate connections between living organisms and their environments, highlighting the beauty and importance of the natural world. Whether you’re a passionate ecologist, a wildlife enthusiast, or simply curious about the wonders of nature, you’ll find a wealth of information and inspiration here. Join us on a journey to uncover the secrets of ecosystems, discover the latest research, and learn how we can all play a part in preserving the incredible diversity of life on our planet.

WILDLIFE

ECOLOGY
Explore Wildlife-Themed Gifts and Our Eco-Friendly Wildlife T-Shirts
Celebrate your love for nature with our exclusive collection of wildlife-themed gifts and eco-friendly wildlife t-shirts. Each item is thoughtfully designed to capture the beauty and spirit of the natural world while staying kind to the environment. Whether you’re searching for the perfect gift for a fellow wildlife enthusiast or want to express your own passion for the wild, our sustainable collection has something special for you. Discover how you can carry a piece of nature with you wherever you go with our beautifully crafted, eco-conscious products.

WILDLIFE LOVERS GIFTS

WILDLIFE T-SHIRTS
-
 Sloth drinking coffee Printed Organic Cotton T-shirt$25.00
Sloth drinking coffee Printed Organic Cotton T-shirt$25.00 -
 Giant Panda Embroidery Organic Cotton T-shirt$35.00
Giant Panda Embroidery Organic Cotton T-shirt$35.00 -
 Koala hugging a tree Embroidered Organic Cotton T-shirt$35.00
Koala hugging a tree Embroidered Organic Cotton T-shirt$35.00 -
 Rhino Conservation T-Shirt Embroidered Rhino protection graphic tees$35.00
Rhino Conservation T-Shirt Embroidered Rhino protection graphic tees$35.00 -
 Protect Penguins T-Shirt: Eco-Friendly Climate Action Apparel Antarctic penguin biologist shirt$29.75
Protect Penguins T-Shirt: Eco-Friendly Climate Action Apparel Antarctic penguin biologist shirt$29.75 -
 Save The Whales Scientific whale illustration tee$29.75
Save The Whales Scientific whale illustration tee$29.75 -
 Bamboo Over Bulldozers: Protect Giant Pandas Panda tee shirt cute$27.75
Bamboo Over Bulldozers: Protect Giant Pandas Panda tee shirt cute$27.75 -
 Cute Hedgehog Embroidered: Love Wildlife, Protect Nature Wildlife conservation tees$35.00
Cute Hedgehog Embroidered: Love Wildlife, Protect Nature Wildlife conservation tees$35.00 -
 Wolf Pack and Moon T-Shirt$35.00
Wolf Pack and Moon T-Shirt$35.00
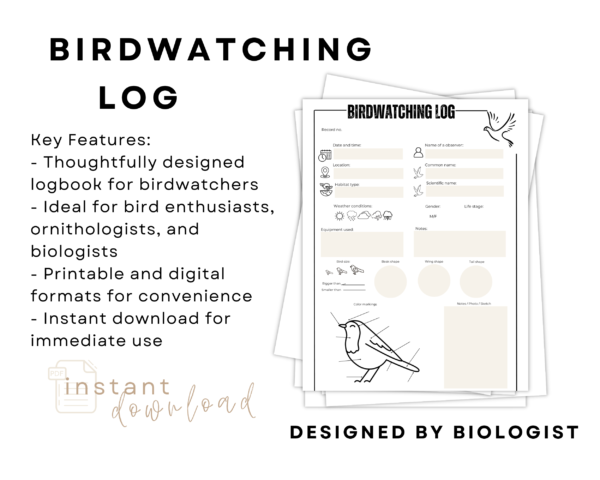
Birdwatching Log
Calling all passionate birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts! Introducing the ultimate Birdwatching Log designed to elevate your avian adventures. Record every detail with precision using our comprehensive log, including: – Record number for organized tracking – Date and time of each observation – Location and habitat type fields for precise recording – Weather conditions during observations – Name of the observer – Species identification for accurate documentation – Size, gender, and life stage details for in-depth observations – Bird features section for noting distinctive characteristics – Color markings part for detailed bird identification – Equipment used section for professional recording -…
Science-Driven Wildlife Insights and Nature Inspired Gift Ideas
- Best Wildlife Biology Degree Programs in the US
 A world-class wildlife biology degree awaits at these top US universities, where research opportunities and field experiences shape tomorrow’s conservationists.
A world-class wildlife biology degree awaits at these top US universities, where research opportunities and field experiences shape tomorrow’s conservationists. - How to Apply for Wildlife Research Grants
 Hope to secure funding for your wildlife research project? Learn the essential steps to craft a winning grant proposal.
Hope to secure funding for your wildlife research project? Learn the essential steps to craft a winning grant proposal. - Grants and Funding Opportunities for Wildlife Research
 Need funding for your wildlife research? Discover millions in grants from regional and national programs with deadlines approaching fast.
Need funding for your wildlife research? Discover millions in grants from regional and national programs with deadlines approaching fast. - How to Become a Wildlife Biologist
 Interested in studying wild animals? Learn the education, skills, and certifications needed to launch an exciting career as a wildlife biologist.
Interested in studying wild animals? Learn the education, skills, and certifications needed to launch an exciting career as a wildlife biologist. - Wildlife Ecology Graduate Programs
 From wildlife conservation to ecological research, discover how graduate programs can transform your passion into a rewarding career protecting nature.
From wildlife conservation to ecological research, discover how graduate programs can transform your passion into a rewarding career protecting nature. - Best Marine Biology Degree Programs in the US
 Breaking waves and marine mysteries await at America’s top oceanography schools, where cutting-edge research meets hands-on coastal exploration.
Breaking waves and marine mysteries await at America’s top oceanography schools, where cutting-edge research meets hands-on coastal exploration. - Best Ecology Bachelor’s in USA
 Hunting for top ecology programs? Discover which U.S. universities offer the best hands-on research opportunities and career-launching environmental degrees.
Hunting for top ecology programs? Discover which U.S. universities offer the best hands-on research opportunities and career-launching environmental degrees. - Best Ecology Graduate Programs in the World
 Uncover top-ranked ecology graduate programs like UC Berkeley’s, offering unparalleled research opportunities and career prospects. Discover more about your future in ecology.
Uncover top-ranked ecology graduate programs like UC Berkeley’s, offering unparalleled research opportunities and career prospects. Discover more about your future in ecology. - Mutualistic Relationships in Nature
 Get a glimpse into the captivating world of mutualistic relationships in nature and discover how these partnerships shape ecosystems.
Get a glimpse into the captivating world of mutualistic relationships in nature and discover how these partnerships shape ecosystems.
- 10 Best Bird Watching Binoculars With Phone Adapter to Enhance Your Nature Experience
 With the right binoculars and phone adapter, you’ll uncover breathtaking moments in nature—discover the top 10 picks that elevate your bird watching experience.
With the right binoculars and phone adapter, you’ll uncover breathtaking moments in nature—discover the top 10 picks that elevate your bird watching experience. - 10 Best Bird Feeders With Camera for Ultimate Backyard Birdwatching Fun
 Learn about the 10 best bird feeders with cameras that enhance backyard birdwatching, but which one will truly transform your viewing experience?
Learn about the 10 best bird feeders with cameras that enhance backyard birdwatching, but which one will truly transform your viewing experience? - 13 Enchanting Wildlife Christmas Ornaments to Bring Nature Indoors This Holiday Season
 Uncover 15 captivating wildlife ornaments that transform your Christmas tree into a magical forest, but which ones will truly enchant
Uncover 15 captivating wildlife ornaments that transform your Christmas tree into a magical forest, but which ones will truly enchant - 15 Adorable Penguin Christmas Decorations to Waddle Up Your Holiday Decor
 Glide into a winter wonderland with these 15 adorable penguin Christmas decorations that’ll transform your home into a frosty paradise. Discover how
Glide into a winter wonderland with these 15 adorable penguin Christmas decorations that’ll transform your home into a frosty paradise. Discover how - 15 Cuddly Reindeer Plush Toys That Will Sleigh Your Heart This Holiday Season
 Snuggle up with adorable reindeer plush toys this holiday season! From classic designs to eco-friendly options, discover 15 cuddly companions that will…
Snuggle up with adorable reindeer plush toys this holiday season! From classic designs to eco-friendly options, discover 15 cuddly companions that will… - 15 Adorable Polar Bear Christmas Ornaments to Melt Your Heart This Holiday Season
 Snuggle up with these 15 heartwarming polar bear Christmas ornaments that’ll transform your tree into an Arctic wonderland, but which one will you choose?
Snuggle up with these 15 heartwarming polar bear Christmas ornaments that’ll transform your tree into an Arctic wonderland, but which one will you choose?
- FLIR C5 Review: Is It Worth the Investment
 Assessing the FLIR C5’s performance, user feedback, and value, we uncover the truth behind this thermal imaging camera’s impressive specs.
Assessing the FLIR C5’s performance, user feedback, and value, we uncover the truth behind this thermal imaging camera’s impressive specs. - Sig Sauer Kilo1000 Monocular Review
 Sophisticated and sleek, the Sig Sauer Kilo1000 Monocular promises exceptional performance, but does it live up to its lofty claims in real-world use?
Sophisticated and sleek, the Sig Sauer Kilo1000 Monocular promises exceptional performance, but does it live up to its lofty claims in real-world use? - MiLESEEY IONJET 2 Range Finder Review
 Scoring high on specs, but does the MiLESEEY IONJET 2 Range Finder deliver accurate distance measurements in the field where it matters most?
Scoring high on specs, but does the MiLESEEY IONJET 2 Range Finder deliver accurate distance measurements in the field where it matters most? - TIDEWE Rangefinder: A Comprehensive Review
 Precise distance measurements and impressive specs make the TIDEWE Hunting Rangefinder a contender, but does it deliver in the field?
Precise distance measurements and impressive specs make the TIDEWE Hunting Rangefinder a contender, but does it deliver in the field? - 4 Best Mist Nets for Bird Research and Conservation in 2024
 Discover the top 15 mist nets for bird research in 2024, but which one will revolutionize your fieldwork? The answer might surprise…
Discover the top 15 mist nets for bird research in 2024, but which one will revolutionize your fieldwork? The answer might surprise… - 15 Best Thermal Imaging Cameras of 2024: Cutting-Edge Heat Detection Reviewed
 Unveiling 2024’s top thermal cameras, this review spotlights cutting-edge heat detection technology that could transform your
Unveiling 2024’s top thermal cameras, this review spotlights cutting-edge heat detection technology that could transform your - 15 Best Rangefinders of 2024: Precision at Your Fingertips
 Grasp the future of precision with our top 15 rangefinders of 2024, offering unparalleled accuracy for hunters and golfers alike. But which one will…
Grasp the future of precision with our top 15 rangefinders of 2024, offering unparalleled accuracy for hunters and golfers alike. But which one will… - 15 Essential Wildlife Camera Trap Accessories for Unparalleled Shots
 Yielding unparalleled shots requires more than just a camera, discover the top 15 essential wildlife camera trap accessories to elevate your photography.
Yielding unparalleled shots requires more than just a camera, discover the top 15 essential wildlife camera trap accessories to elevate your photography. - LaMotte R-3633-05 Freshwater Aquaculture Kit Review
 Precise water quality monitoring awaits, but does the LaMotte R-3633-05 Freshwater Aquaculture Kit deliver on its promises?
Precise water quality monitoring awaits, but does the LaMotte R-3633-05 Freshwater Aquaculture Kit deliver on its promises?

Nature and Animal Lover? Shop Our Products!
Sustainable and eco-friendly products that support meaningful conservation projects.

Erzsebet Frey (Eli Frey) is an ecologist and online entrepreneur with a Master of Science in Ecology from the University of Belgrade. Originally from Serbia, she has lived in Sri Lanka since 2017. Eli has worked internationally in countries like Oman, Brazil, Germany, and Sri Lanka. In 2018, she expanded into SEO and blogging, completing courses from UC Davis and Edinburgh. Eli has founded multiple websites focused on biology, ecology, environmental science, sustainable and simple living, and outdoor activities. She enjoys creating nature and simple living videos on YouTube and participates in speleology, diving, and hiking.