Do you ever wonder why some animals have such big feet? Well, get ready to explore the fascinating world of animals with big feet.
From the majestic elephants to the agile jacanas, these creatures have evolved to thrive in various environments.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of big feet, their adaptations, and the correlation between foot size and body size.
Discover how human activities impact these unique adaptations and the need for conservation efforts.
Get ready to embark on a scientific journey through the animal kingdom!
Key Takeaways
- Animals with big feet have adaptations that allow them to navigate different terrains and environments.
- Big feet provide stability, balance, and help distribute weight, reducing pressure on delicate surfaces.
- Foot size and shape vary among species, often correlating with their ecological niche and lifestyle.
- Human activities, such as habitat destruction and pollution, can impact animal foot adaptations and threaten species with specialized feet.
Elephants
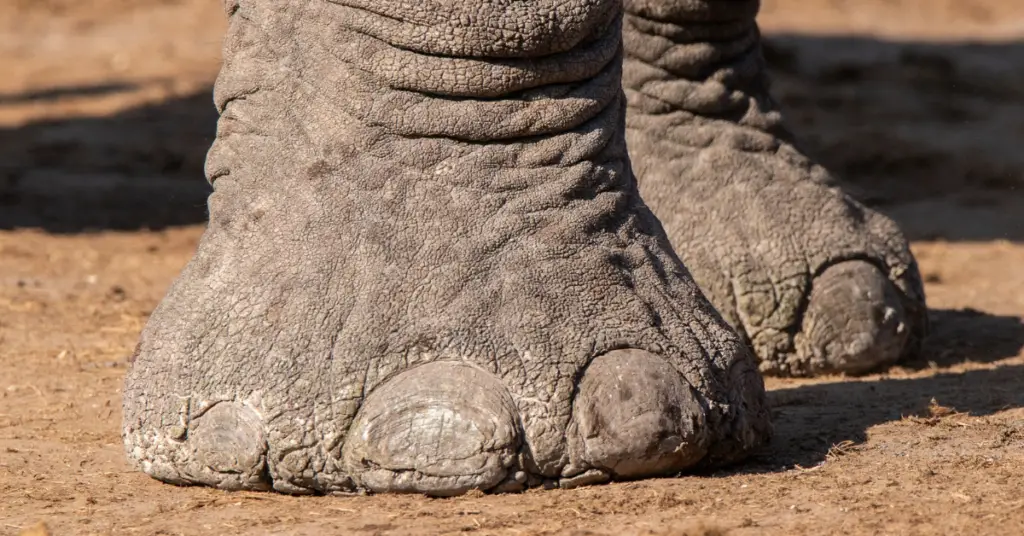
Elephants have existed on Earth for millions of years. These magnificent creatures are known for their large size and distinct features, including their big feet. Elephant conservation plays a crucial role in ensuring the survival of these remarkable animals. One important aspect of elephant conservation is foot care.
Elephants have fleshy, tough-skinned feet cushioned with thick pads. These adaptations allow them to walk long distances and support their massive body weight. However, their feet are also susceptible to various health issues, such as cracks, infections, and abscesses. To address these concerns, conservation efforts focus on providing elephants with proper foot care.
Elephant foot care involves regular inspections and treatments by trained professionals. This includes cleaning, trimming overgrown nails, and applying ointments to keep the skin moisturized and prevent infections. Additionally, elephants may receive foot baths to soothe any discomfort or inflammation.
Maintaining healthy feet is essential for elephants to move freely, forage for food, and engage in social interactions. By prioritizing elephant foot care, conservation organizations contribute to the overall well-being and longevity of these extraordinary animals.
Ostriches
Continuing with our exploration of animals with big feet, let’s now turn our attention to ostriches, fascinating creatures known for their remarkable size and impressive foot adaptations. Ostriches, the largest flightless birds on the planet, possess unique locomotion abilities that allow them to navigate their diverse habitats with ease. Here are some key facts about ostriches and their feet:
- Habitat and Distribution: Ostriches are native to the savannas and grasslands of Africa. They’re found in countries such as Kenya, Tanzania, and South Africa. Ostriches have adapted to various environments, including deserts, woodlands, and semi-arid regions.
- Water Walking Adaptation in Basilisks: While not directly related to ostriches, it’s interesting to note that some animals, like the water-running basilisks found in tropical forests of Mexico and South America, have developed the ability to walk on water. This adaptation allows them to escape from predators and search for food in aquatic habitats.
- Impact of Climate Change: Climate change can have significant effects on the habitats of ostriches and other animals. Alterations in temperature and precipitation patterns may lead to changes in vegetation cover and availability of resources, which can indirectly impact the locomotion and survival of ostriches.
- Importance of Even Weight Distribution: Ostriches have large, powerful feet that aid in their running and walking abilities. The even distribution of weight across their feet is crucial for maintaining balance and stability while moving at high speeds. This adaptation helps ostriches avoid injuries and efficiently navigate their surroundings.
Jacanas
Jacanas, a unique group of birds, possess fascinating foot adaptations.
These small birds are known for their long toes, which enable them to navigate through floating vegetation in swamps, shallow lakes, and lagoons.
The length and flexibility of their toes allow jacanas to distribute their weight evenly, allowing them to walk on lily pads without sinking.
Unique Foot Adaptations
If you’re curious about animals with unique foot adaptations, one example you might find fascinating is the jacana. These birds have developed specialized feet that allow them to navigate their habitats with ease.
Here are two interesting foot adaptations in jacanas:
- Long Toes: African jacanas have exceptionally long toes that help them walk on floating vegetation, such as lily pads. Their toes distribute their weight evenly, preventing them from sinking into the water. This adaptation allows jacanas to access food sources that other birds can’t reach.
- Climate Change Impact: Climate change can have a significant impact on the foot adaptations of jacanas. Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns can lead to changes in the vegetation and water levels in their habitats. This may affect the availability of floating vegetation, which jacanas rely on for foraging and nesting. As a result, jacanas may need to adapt their foot structure or behavior to cope with these changes.
Jacanas exemplify the remarkable ways in which animals have evolved unique foot adaptations to thrive in their environments.
Habitat Preferences and Feet
As we delve into the topic of habitat preferences and feet, it’s important to consider how jacanas have evolved their unique foot adaptations to thrive in specific environments.
Jacanas are highly specialized birds known for their large feet proportionate to their body size. These adaptations allow them to walk on lily pads and distribute their weight evenly, enabling them to navigate the swamps, shallow lakes, and lagoons they inhabit.
The habitat preferences of jacanas are closely tied to their foot adaptations, as their long toes help them navigate the floating vegetation in their environment. However, it’s worth noting that the impact of climate change on animal foot function can’t be overlooked.
Changes in temperature, water levels, and vegetation patterns may pose challenges for jacanas and their ability to effectively use their specialized feet. Continued research is crucial to understanding how these adaptations may be affected and to inform conservation efforts to protect these unique birds and their habitat preferences.
Importance of Even Weight Distribution?
To understand the importance of even weight distribution, consider how jacanas utilize their unique foot adaptations.
Jacanas, found in swamps, shallow lakes, and lagoons, have the largest feet proportionate to their body size among all animals. Their feet are long and slender, with elongated toes that allow them to walk on floating vegetation.
The importance of even weight distribution in animals with big feet can’t be overstated. It plays a crucial role in providing stability, balance, and reducing pressure on delicate surfaces. Even weight distribution enables jacanas to navigate their watery habitats with ease, without sinking into the vegetation.
However, human activities such as habitat destruction and pollution can disrupt their foot adaptations and jeopardize their survival. Conservation efforts are therefore essential to protect these animals and preserve their unique foot adaptations.
Polar Bears
Polar bears, known for their massive size and powerful presence, have unique foot adaptations that allow them to thrive in their icy habitat.
These adaptations include large, wide paws with non-retractable claws, providing them with excellent traction on ice and snow. Additionally, their feet are covered in thick fur, acting as insulation against the freezing temperatures.
The impact of climate change on polar bears and their foot function is a growing concern, as melting ice threatens their ability to hunt and swim effectively.
Polar Bear Foot Adaptations
Adaptation plays a crucial role in the survival of animals. When it comes to their feet, polar bears have developed remarkable characteristics. These adaptations are especially important for their swimming techniques and to cope with the impact of climate change on their feet.
Polar bear swimming techniques:
- Polar bears are excellent swimmers and rely on their large, webbed paws to propel themselves through the water.
- Their feet are designed to act like paddles, providing maximum surface area for effective propulsion.
Impact of climate change on polar bear feet:
- As climate change causes the Arctic ice to melt at an alarming rate, polar bears are facing new challenges.
- With less sea ice available for hunting, they’re forced to swim longer distances, putting more strain on their feet.
- The increased exposure to water can lead to prolonged contact with cold temperatures, which can result in frostbite and other foot-related issues.
Impact of Climate Change
The impact of climate change on the feet of polar bears is significant and poses a threat to their survival and well-being.
Polar bears are highly adapted to their Arctic environment, with unique locomotion abilities that rely on their large, wide-padded feet. These feet provide traction and stability on the icy terrain, allowing them to walk, run, and hunt effectively.
However, as the Arctic sea ice melts due to rising temperatures, polar bears are facing challenges. The reduction in sea ice limits their access to prey, forcing them to swim longer distances to find food. Prolonged swimming can lead to fatigue and physical stress, causing injuries to their feet.
Additionally, the thinning ice increases the risk of polar bears falling through, further endangering their foot health.
The impact of climate change on the feet of polar bears underscores the urgent need for conservation efforts to mitigate its effects on these iconic Arctic predators.
Swimming and Hunting Techniques
As you explore the swimming and hunting techniques of polar bears, it’s evident that their large, wide-padded feet play a crucial role in their survival in the Arctic environment. These remarkable adaptations allow polar bears to navigate the icy waters and capture their prey effectively.
Here are some key points to understand their swimming techniques and hunting strategies:
Swimming Techniques:
- Polar bears are excellent swimmers, capable of covering long distances in the frigid Arctic waters.
- Their large feet act as powerful paddles, providing propulsion and maneuverability in the water.
- The wide pads on their feet distribute their weight, preventing them from sinking into the thin ice.
- Polar bears use a combination of front paw strokes and powerful kicks to propel themselves forward.
Hunting Strategies:
- Polar bears primarily hunt seals, their main source of food in the Arctic.
- They use their large feet to silently approach seal breathing holes in the ice.
- By spreading their weight over a large surface area, polar bears can distribute their weight evenly, reducing the risk of breaking the ice and alerting their prey.
- Once in close proximity to a seal, polar bears rely on their strong forelimbs and sharp claws to grab and secure their prey.
Jerboas
If you’re curious about animals with big feet, one species that stands out is the jerboa. Jerboas are small rodents that belong to the family Dipodidae, and they’re known for their unique feeding habits and survival strategies.
These fascinating creatures are found in the hot regions of North Africa, Europe, and Asia. Jerboas have adapted to their arid environments by developing long hind legs and elongated feet, which allow them to move quickly and efficiently across sandy terrain.
Their big feet serve as excellent adaptations for jumping, as jerboas are capable of leaping up to 10 feet in a single bound. This ability helps them escape from predators and reach food sources in their harsh habitats.
Jerboas also have specialized feeding habits, primarily consuming seeds, insects, and plant material. Their big feet aid in locating and capturing prey, as well as digging for food in the desert sand.
These unique feeding habits and survival strategies make jerboas a fascinating example of animals with big feet.
Kangaroos
To learn more about animals with big feet, let’s explore the unique characteristics of kangaroos.
- Kangaroo Jumping Abilities:
- Kangaroos are renowned for their exceptional jumping abilities, allowing them to cover great distances in a single bound.
- Their large hind feet, equipped with strong muscles and tendons, serve as powerful springs that propel them forward.
- Kangaroos can jump as high as 30 feet and as far as 25 feet in a single leap, enabling them to navigate their vast Australian habitats efficiently.
- Their front limbs, although much smaller than their hind limbs, aid in stabilizing their landing and maintaining balance during rapid movements.
- Impact of Climate Change on Kangaroo Habitats:
- Climate change poses significant challenges to kangaroo habitats.
- Rising temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can lead to the degradation and loss of their preferred grassland habitats.
- Reduced availability of food and water sources can negatively impact kangaroo populations.
- Additionally, increased frequency and intensity of wildfires, a consequence of climate change, can further disrupt kangaroo habitats and result in habitat fragmentation.
Kangaroos exemplify the remarkable adaptability of animals with big feet. Their exceptional jumping abilities allow them to thrive in their unique environments. However, the impact of climate change on their habitats highlights the vulnerability of these fascinating creatures. Efforts to mitigate climate change and preserve their habitats are crucial for the long-term survival of kangaroos and other animals with big feet.
Emus
The Emus, flightless birds with three toes on each foot, are another fascinating example of animals with big feet. Emus are native to Australia and are the second-largest living bird species in the world, reaching heights of up to 6.2 feet. Their unique foot structure and function contribute to their ability to run at speeds up to 31 miles per hour.
Emus have long, powerful legs that are adapted for running across varied terrain. Each foot has three toes, with the central toe being the longest and most prominent. The toes are equipped with sharp claws that aid in traction and defense. Emus use their feet to rapidly propel themselves forward, using a combination of powerful strides and quick foot movements. This efficient foot structure allows them to cover long distances and escape from predators.
Conservation efforts play a crucial role in protecting emus and their unique foot adaptations. Emus have faced habitat loss and fragmentation due to human activities, such as agriculture and urbanization. Additionally, they’ve been hunted for their feathers and meat. Conservation organizations are working to preserve emu populations and their habitats through habitat restoration, captive breeding programs, and public awareness campaigns.
Understanding the unique foot structure and function of emus highlights the importance of conservation efforts in preserving the biodiversity of our planet. By protecting animals with big feet like emus, we can ensure the survival of these fascinating species and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Snowshoe Hares
Moving on to Snowshoe Hares, these animals with big feet are known for their impressive speed and agility in snowy environments. Snowshoe hares have adapted to their habitat by developing large, furry feet that act as natural snowshoes, allowing them to move swiftly across deep snow without sinking.
Here are some interesting facts about snowshoe hares:
- Camouflage: Snowshoe hares have a coat that changes color with the seasons. In winter, their fur becomes white to blend in with the snow, providing them with excellent camouflage against predators like polar bears. However, with the impact of climate change on polar bears and the decrease in snow cover in some areas, this adaptation may become less effective.
- Speed and Agility: Snowshoe hares are incredibly fast and agile. They can reach speeds of up to 27 miles per hour and have the ability to change direction quickly, allowing them to escape from predators such as lynx and foxes.
- Feeding Habits: Snowshoe hares primarily feed on the bark, twigs, and buds of trees and shrubs. Their large feet help them navigate through deep snow to reach their food sources, even in harsh winter conditions.
- Reproduction: Snowshoe hares have a high reproductive rate, with females capable of producing several litters in a single year. This adaptation ensures the survival of their species, even in challenging environments.
Water-Running Basilisks
Water-Running Basilisks, also known as Jesus Christ lizards, have developed a remarkable adaptation that allows them to walk on water. Their long toes are equipped with fringed scales that create air pockets, increasing surface tension and preventing them from sinking.
This unique locomotion ability enables them to navigate their tropical forest habitat in Mexico and South America, where they can escape predators or search for food by skimming across the water’s surface.
Water-Walking Adaptation in Basilisks
You can observe a fascinating water-walking adaptation in basilisks. These creatures, also known as water-running basilisks, have developed unique swimming techniques and ecological adaptations to navigate their watery habitats.
- Swimsuit-like Skin:
- Basilisks have specialized skin that allows them to skim across the water’s surface. Their scales create a hydrophobic layer that repels water, reducing drag and enabling them to move swiftly.
- This adaptation helps basilisks maintain their balance and stability while walking on water, allowing them to escape predators or search for food.
- Long Toes and Fringed Feet:
- Basilisks possess elongated toes with fringed edges, which increase their surface area when in contact with the water.
- This design helps distribute their weight more evenly, enabling them to create enough buoyancy to stay afloat and walk on water without sinking.
Through these unique adaptations, basilisks have evolved to become masterful water-walkers, showcasing their remarkable ability to traverse their aquatic environments with grace and agility.
Unique Locomotion Abilities
One fascinating characteristic of water-running basilisks is their impressive ability to traverse their aquatic environments with grace and agility, utilizing unique locomotion abilities. These basilisks, also known as Jesus lizards, have evolved specialized adaptations for both land and water, allowing them to navigate their surroundings with remarkable efficiency.
When running on water, they employ a distinctive high-speed stride, where they rapidly slap their feet on the water’s surface. This motion creates air pockets that generate lift and support their weight, enabling them to move across water for short distances. This remarkable locomotion ability not only aids in their escape from predators but also facilitates their unique hunting strategies.
Water-running basilisks have adapted to extreme environments, and their ability to walk on water showcases the remarkable adaptations that animals can develop to thrive in their habitats.
Habitat and Distribution?
Water-running basilisks inhabit tropical forests of Mexico and South America. These fascinating creatures have specific habitat preferences that allow them to thrive in their environment.
Here are some key points about their habitat and distribution:
- Preferred Habitat:
- Water-running basilisks are primarily found near freshwater sources such as rivers, streams, and ponds.
- They prefer dense vegetation and trees along the water’s edge for shelter and protection.
- These basilisks are excellent climbers and can often be seen perched on branches or basking in the sun.
- Distribution:
- Water-running basilisks are native to the tropical forests of Mexico and South America.
- They can be found in countries like Costa Rica, Panama, Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador.
- Their distribution is influenced by the availability of suitable water bodies and forested areas.
Impact of Human Activities:
- Habitat Destruction:
- Deforestation and urbanization pose significant threats to the habitat of water-running basilisks.
- Clearing of forests for agriculture and logging disrupts their natural habitat, leading to population decline.
- Pollution:
- Water pollution from industrial activities and agricultural runoff can negatively impact the water quality of their habitat.
- Contaminated water can affect the health and survival of these basilisks, as well as their prey.
It is crucial to recognize the importance of preserving the habitat of water-running basilisks and implementing conservation measures to ensure their survival in the face of ongoing human activities.
American Coots
The American Coots have lobed toes for walking on aquatic vegetation. These birds have four toes, with three in the front and one in the back. Their feet aren’t webbed like other aquatic birds, allowing them to have versatile movement in various aquatic habitats. American coots use their feet in prey capture by foraging for small aquatic invertebrates such as insects, snails, and crustaceans. Their lobed toes help them navigate through vegetation and capture their prey with precision.
Climate change can have significant effects on the habitat and distribution of American coots. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, the availability of suitable aquatic vegetation and water resources may change. This can impact the food availability and nesting sites for American coots, affecting their overall population and distribution.
Furthermore, climate change can also lead to habitat loss and degradation. Rising sea levels, increased droughts, and extreme weather events can result in the loss of wetland habitats that American coots rely on. Changes in water quality and temperature can also have detrimental effects on the survival and reproductive success of these birds.

Erzsebet Frey (Eli Frey) is an ecologist and online entrepreneur with a Master of Science in Ecology from the University of Belgrade. Originally from Serbia, she has lived in Sri Lanka since 2017. Eli has worked internationally in countries like Oman, Brazil, Germany, and Sri Lanka. In 2018, she expanded into SEO and blogging, completing courses from UC Davis and Edinburgh. Eli has founded multiple websites focused on biology, ecology, environmental science, sustainable and simple living, and outdoor activities. She enjoys creating nature and simple living videos on YouTube and participates in speleology, diving, and hiking.